

Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences
DOI: 10.58739/jcbs/v14i1.24.24
Year: 2024, Volume: 14, Issue: 1, Pages: 13-18
Original Article
Harish Rangareddy1,*, Shashidhar Kurpad Nagaraj2, Prabhavathi Kannala3
1 Assistant Professor, Department of Biochemistry, Haveri Institute of Medical Sciences, Haveri, Karnataka, India
2 Professor, Department of Biochemistry, Sri Devaraj Urs Medical College constituent college of Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education and Research, Karnataka, India
3 Professor & HoD, Department of Biochemistry, Sri Devaraj Urs Medical College constituent college of Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education and Research, Karnataka, India
*Corresponding author email: [email protected]
Received Date:26 March 2024, Accepted Date:01 April 2024, Published Date:12 April 2024
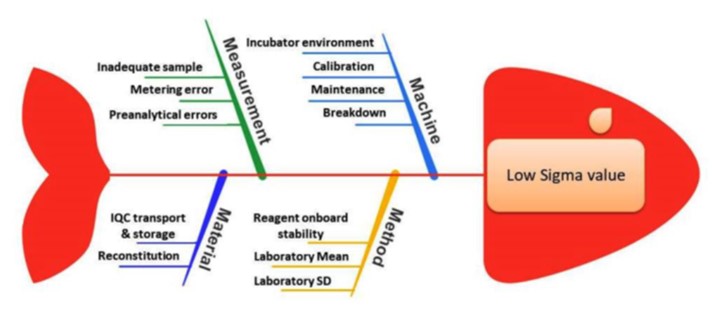
Background: The Six Sigma methodology has become a standard in quality assessment and management, widely adopted in various industries since the mid-1980s. This methodology is applicable wherever the outcome of a process needs measurement. One area where Sigma metrics find utility is in laboratory services, particularly in evaluating the quality assurance of biochemical parameters. Aims: This study aimed to measure and analyze the sigma metrics of thyroid hormones T3, T4, and TSH within the framework of NABL accreditation (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories). Materials & Methods: The study was designed as a retrospective observational study, utilizing quality control data from the Clinical Biochemistry section spanning from January 2021 to December 2021 retrieved from laboratory records. The data considered included Bio-Rad Lyphochek Immunoassay Internal Quality Control (IQC) Control and Bio-Rad External Quality Assurance Scheme (EQAS) Immunoassay monthly program data. Calculations for Coefficient of variation (CV %), Bias %, and Total Error allowable (TEa) were made to derive the sigma metric. The formula used for sigma calculation was Sigma Σ(σ) = (TEa% - Bias%) / CV%, while the Quality Goal Index (QGI) ratio was determined using the formula QGI = Bias / 1.5CV. Results: The results categorized the assay performance based on sigma levels: >6 denoted world-class performance, 5-6 indicated excellence, 4-5 represented good performance, 3-4 was deemed acceptable, and 2-3 signified poor performance. All analytes demonstrated sigma levels below 6 (2.61-5.85) varying from poor to excellent and the QGI was below 0.8, indicating a need to enhance the precision of assays. Conclusion: The Six Sigma metric analysis serves as a benchmark tool that can aid laboratories in enhancing assay performance, formulating protocols for Internal Quality Control (IQC), and evaluating existing laboratory procedures.
Keywords
Six sigma, Quality Goal Index, Internal Quality Control
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education, Kolar, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.