

Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences
DOI: 10.58739/jcbs/v15i2.24.178
Year: 2025, Volume: 15, Issue: 2, Pages: 126-132
Original Article
Sonane Madhavi1, Saxena Sangeeta1∗
1Department of Biotechnology, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Vidya Vihar, Rae Bareli Road, Lucknow, 226025, Uttar Pradesh, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:17 October 2024, Accepted Date:15 April 2025, Published Date:13 July 2025
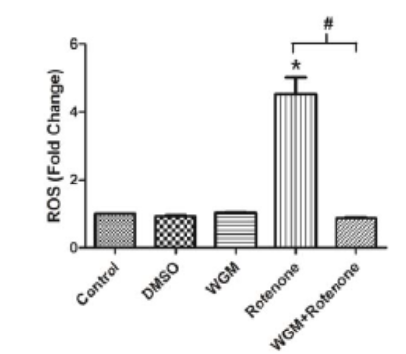
Background: Wheatgrass (Triticum, Family: Poaceae) juice is considered as a living food and often consumed due to its countless health benefits. Wheatgrass juice contains many bioactive compounds which can be useful for ameliorating neurogenerative diseases. Wheat in the form of microgreen (7th day after sowing) have been reported to have higher level of bioactive compounds compared to the mature wheatgrass or grain. Objective: To evaluate the protective effects of wheat microgreen extract against rotenone induced neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. Methods: Worms were exposed to the different concentrations of rotenone to determine the concentration that can induce neurodegeneration without causing any mortality. Wheat microgreen extract was exposed to worms along with rotenone to determine the effective concentration. Neuroprotective potential of wheat microgreen extract was assessed by foraging and locomotory performance, free radical generation, cytotoxicity assay and dopamine content. Results: 4 µM concentration of rotenone was found non lethal but able to induce behavior changes after 48 h of exposure. Wheat microgreen extract at 1 mg/mL concentration was found minimum and effective when exposed along with rotenone to worms. Rotenone exposed C. elegans were observed to have reduced locomotory and foraging behaviors along with dopamine content, while an increased level of free radical and cytotoxicity. Wheat microgreen extract improved behavior performance and dopamine content, also reduce free radical generation and cytotoxicity in the rotenone exposed worms. Conclusion: Our study concludes that wheat microgreen exhibits neuroprotective and antioxidant potential and can be considered as a possible treatment for neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Wheat microgreen; Caenorhabditis elegans; Neurodegeneration; Rotenone
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education, Kolar, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.