

Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences
Year: 2025, Volume: 15, Issue: 1, Pages: 49-54
Original Article
Ahlawat Poonam1, Sharma Parul2∗, Tyagi Nicky2
1Associate Professor, Faculty of Nursing, SGT University, Gurugram, Haryana, India
2PG Tutor, Faculty of Nursing, SGT University, Gurugram, Haryana, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:04 October 2024, Accepted Date:11 January 2025, Published Date:25 March 2025
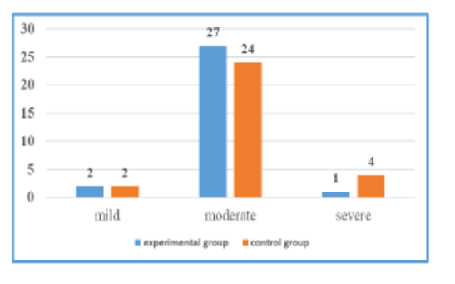
Background: Academic procrastination which is a kind of procrastination includes delaying school based tasks and can be described as procrastinating academic tasks due to some reason. Objectives of the study are to assess the pre intervention level of academic procastinaton and time management skills among B.Sc nursing students; To assess the effectiveness of educational module on academic procrastination and time management skills among the B.Sc nursing students and; To find out the level of association between post test scores with selected demographic variables among the B.Sc nursing students, SGT university, Gurugram. Materials & Methods: The researcher adopted the quantitative research approach with Quasi experimental research design and Convenient sampling technique. The setting of the study was faculty of nursing, SGT University, Gurugram, Haryana. The present study's sample included 60 nursing students. The tool used in this study was organized into 2 sections. Section A included the Demographic profile of nursing students. Section-B includes the Semi structured questionnaire. Descriptive and inferential statistics was used. Results: The results shows that the pre test mean score (39) and standard deviation (7.2) in experimental group and pre test mean score is 37 with SD (9.1) in control group and after the intervention the post test mean score (50) and standard deviation (3.8) in experimental group and the post test mean score (39) and standard deviation (9.8) in control group. The obtained ‘t’ value in pre-test of experimental group and control group is 0.484 which is less than table value (2.009). As in post-test t- value is 5.413 which is more than the table value and is significant which shows that intervention was effective. The result related to association with selected demographic variables shows that the year of study and time duration to reach home after college significant at 0.05 level of significance. Through a comprehensive analysis of procrastination behavior among students, several key insights have emerged. Conclusion: By implementing targeted interventions aimed at enhancing self-regulation skills, promoting adaptive coping strategies. Students get better understanding of academic procrastination.
Keywords: Academic procrastination, Time management skills, Educational module
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education, Kolar, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.