

Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences
DOI: 10.58739/jcbs/v15i3.25.35
Year: 2025, Volume: 15, Issue: 3, Pages: 218-221
Original Article
Reddy Yeduguri Jahnavi1, Kalyani R R2∗, Prabhakar K3
1Senior Resident, Pathology, SDUMC, Kolar, Karnataka, India
2Head and Director, R & D, SDUMC, Kolar, Karnataka, India
3Dean and Principal, SDUMC, Kolar, Karnataka, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:17 May 2024, Accepted Date:12 June 2025, Published Date:26 September 2025
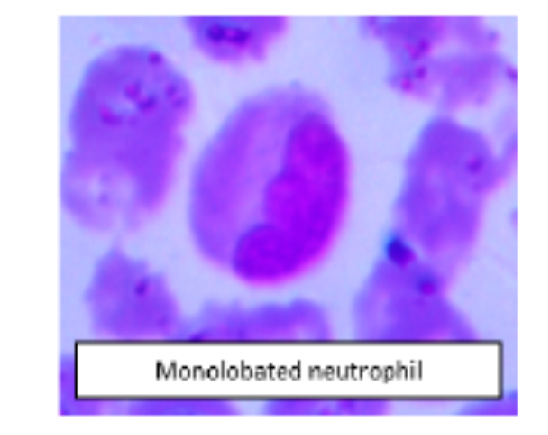
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a newly diagnosed viral disease first identified China in December 2019 .The primary route of infection is by respiratory droplets and aerosols which enters into the cell. The lethal effects are due to the activation of renin angiotensin aldosterone pathway in the cell which further activates immune system and presents as lymphopenia in cases which have severe viral load. A few studies are available in English literature regarding quantitative parameters of peripheral blood, but very minimal data is available regarding morphological changes in blood smear. Hence this study was taken up to study morphological changes in the peripheral smears of patients with Covid-19. Objectives: To evaluate peripheral blood smears cell morphology in RT PCR confirmed cases of Covid19. Materials and Methods: All the cases were studied for a period of 3 months (May, June, July 2021) at Central Diagnostic Laboratory Services, RLJ Hospital, SDUMC, Kolar, Karnataka. Peripheral blood smears were made from all the blood samples which were collected in EDTA vacutainers, stained with Leishman stain and studied for morphological features of all three cell lines in the smear. Individual morphologies were noted. Results: Majority of the smears showed neutrophilia and lymphopenia with shift to left of neutrophilis. The morphological features seen in WBC’s in neutrophilis are hypersegmentation, monolobulated neutrophils, band forms, pyknotic nucleus, ring, fetal forms, toxic granules and cytoplasmic vacuoles. Conclusion: Our study identifies and describes significant morphologic changes in the peripheral blood cells of COVID 19 patients. An understanding of these morphologic changes in addition to established hematologic parameters can aid in the diagnosis of COVID-19. Peripheral smear review may help with management decisions in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: Covid-19, Peripheral blood smear, Morphological Changes
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education, Kolar, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.