

Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences
DOI: 10.58739/jcbs/v15i3.24.251
Year: 2025, Volume: 15, Issue: 3, Pages: 180-183
Original Article
Tole S B1∗, Joshi A A1, Gat R R1, Dhaka S S1, Ghagare A D1
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, ASPM’s K. T. Patil College of Pharmacy, Dharashiv, Maharashtra, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:24 December 2024, Accepted Date:03 March 2025, Published Date:25 September 2025
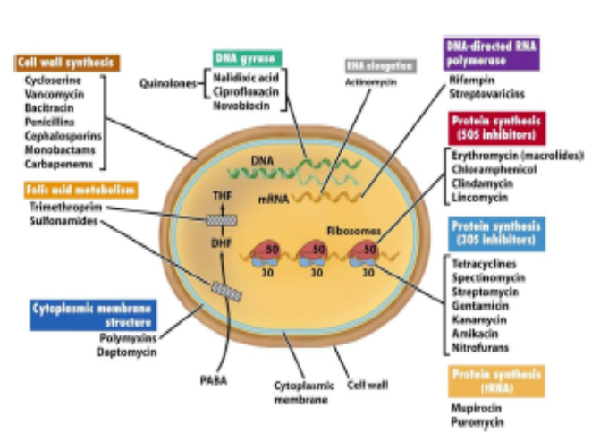
Background: The study examined the prescribing patterns of antibiotics in pediatric patients at the Civil Hospital, Dharashiv, Maharashtra. It aimed to understand the demographic and clinical factors influencing antibiotic use and assess adherence to Standard Treatment Guidelines (STG). Objectives: The objectives were to investigate the prescription practices for antibiotics in pediatric patients, evaluate the factors such as age, weight, and disease condition, and analyze compliance with the STG. Methods: This prospective observational study was conducted at the pediatric department of the Civil Hospital, Dharashiv, from August 2023 to March 2024. Data were collected from 120 pediatric patients through chart reviews, administrative database analysis, and interviews during ward rounds. The collected data were analyzed to identify trends and patterns in antibiotic prescription. Results: Among the 120 pediatric cases, the most prescribed antibiotic was Penicillin (45.23%), followed by Cephalosporins (23.36%), Aminoglycosides (16.35%), and Quinolones (7.47%). Viral infections were the most prevalent condition (41.66%), followed by upper respiratory tract infections (25.83%) and gastrointestinal tract infections (9.16%). Empiric treatment was the most common approach (77.5%), while definitive and prophylactic treatments were used in 16.66% and 5.83% of cases, respectively. The majority of patients were from rural areas (55%), and intravenous administration was the most frequent route (45.81%). Conclusion: The study highlighted the prescribing patterns of antibiotics in pediatric patients, emphasizing the need for rationalization of antibiotic use. The findings underscore the importance of adherence to STG to minimize resistance and ensure effective treatment outcomes.
Keywords: Antibiotics, Pediatrics, Rational Prescribing, Penicillin, Amoxicillin
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education, Kolar, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.