

Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences
DOI: 10.58739/jcbs/v15i3.25.77
Year: 2025, Volume: 15, Issue: 3, Pages: 204-210
Original Article
Joshi Vineet1∗, Raja Md. Hussain1, Dobhal Kiran2
1College of Pharmacy, Shivalik Campus Dehradun, 248197, Uttarakhand, India
2Assistant professor, College of Pharmacy, Shivalik Campus, Dehradun, 248197, Uttarakhand, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:25 March 2025, Accepted Date:15 April 2025, Published Date:26 September 2025
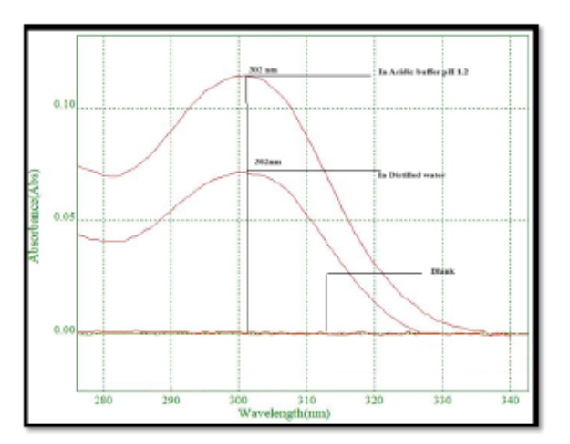
Background: This study investigates establishing a novel therapeutic approach to treating peptic ulcers that uses an in-situ gel microsponge incorporating esomeprazole. Microsponges carrying esomeprazole magnesium, ethyl cellulose, and Eudragit RS-100 were developed via a quasi-emulsion solvent diffusion technique. Methods: Five formulations were developed and analyzed for entrapment efficiency, drug content, yield, and particle size. Results: From all the five formulations, the F3 formulation showed the maximum results in terms of high drug content (85.24%), entrapment efficacy (85.67 %), particle size (8.36±0.43 µm), and production yield (87.35%). Then the microsponges were incorporated with the Poloxamer 188 to form in-situ gel. The formulation (F3) demonstrated appropriate viscosity (38cps), gelling time (11.95±0.56 sec), and gelling capacity (++). The in-vitro drug release profile revealed that formulation F3 exhibited an extended drug release rate (92.18%). Stability studies indicated minimal changes in particle size (8.36±0.43) and entrapment efficiency (85.67) over three months. Conclusion: This innovative Esomeprazole-loaded microsponge in- situ gel formulation is promising to enhance drug delivery, prolong drug release, and improve patient compliance in peptic ulcer therapy.
Keywords: Microsponge, Esomeprazole, Gastric, Peptic Ulcer, In-situ gel
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education, Kolar, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.