

Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences
DOI: 10.58739/jcbs/v15i3.24.221
Year: 2025, Volume: 15, Issue: 3, Pages: 163-171
Original Article
Mukherjee Prathana1, Das Partha Ranjan2∗, Pradhan Deepak Kumar2, Sahoo Rajesh3, Mishra Priyadarshini4
1In-charge Physiotherapist, Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine, Kolkata, West Bengal, India
2Assistant professor, Abhinav Bindra Sports Medicine and Research Institute (ABSMARI), Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
3Junior Occupational Therapist, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Puducherry, India
4Associate Professor, Abhinav Bindra Sports Medicine and Research Institute (ABSMARI), Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
[email protected]
Received Date:21 November 2024, Accepted Date:15 April 2025, Published Date:25 September 2025
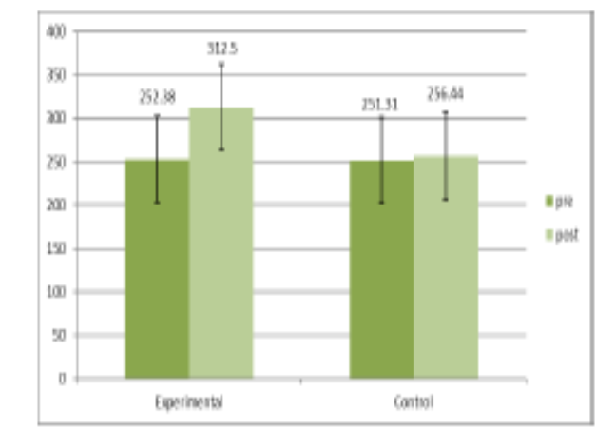
Background: Children with cerebral palsy (CP) often experience reduced cardiopulmonary endurance and physical activity levels, which can lead to long-term health complications. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of aerobic exercise combined with conventional physiotherapy on cardiopulmonary endurance in children with CP. Methods: A two-group experimental pretest post-test design was utilized, involving 32 children aged 4 to 14 years diagnosed with CP at GMFCS levels I and II. Participants were randomly assigned to an experimental group, which received aerobic exercises in addition to conventional physiotherapy, and a control group that received only conventional physiotherapy. The intervention lasted six weeks, with assessments conducted before and after the treatment period. Key outcome measures included the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), walking speed, heart rate, and energy expenditure index (EEI). Results: The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in the distance covered during the 6MWT, walking speed, and EEI compared to the control group. Statistical analysis revealed that the inclusion of aerobic exercises led to more pronounced enhancements in cardiopulmonary endurance and overall physical capabilities. Conclusion: The findings suggest that aerobic exercise, when integrated into rehabilitation programs for children with CP, significantly improves cardiopulmonary endurance and physical fitness. This study supports the incorporation of structured aerobic training as a vital component of therapeutic interventions, promoting better health outcomes and quality of life for children with cerebral palsy.
Keywords: Aerobics, Cerebral palsy, Physical activity, Physical fitness
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education, Kolar, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.