

Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences
DOI: 10.58739/jcbs/v15i2.24.187
Year: 2025, Volume: 15, Issue: 2, Pages: 118-125
Original Article
Febeena K R1∗, Kurian Cini2
1Research Scholar, School of Computer Sciences, Mahatma Gandhi University, Kottayam, Kerala, India
2Principal, Al-Ameen College, Edathala, Aluva, Kerala, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:17 October 2024, Accepted Date:12 December 2024, Published Date:11 July 2025
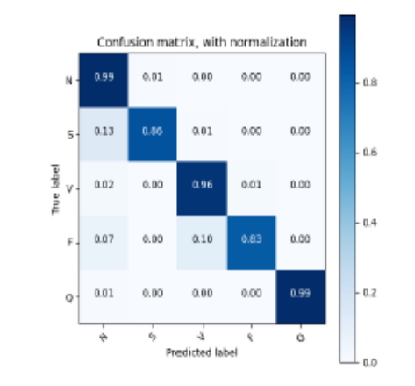
Background: The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a vital clinical signal for recognizing cardiovascular ailments (CVDs) such as Arrhythmia. However, manual assessment of ECG signals is challenging due to subtle physiological variations in both regular and irregular cases, mainly when dealing with a large volume of cardiac patients. From this perspective, automated sorting of ECG signals can offer substantial relief to healthcare experts, facilitating precise analysis. Objective: This study aims to develop an automated system for sorting ECG signals to ease the workload of healthcare experts and enhance the precision of cardiac condition analysis. The ultimate goal is to provide healthcare professionals with a reliable tool that streamlines the interpretation process, enabling timely and accurate diagnoses, thereby improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare burdens. Method & Material: Current approaches predominantly rely on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to extract ECG signal features. However, these may fail to capture nuanced differences in pathological features across different diseases. Transformer networks, known for their prowess in handling sequence data, offer advantages in feature extraction but often rely on extensive datasets, making the complete network intricate. This proposed model utilizes CNN and Transformers for arrhythmia classification. This study was conducted on the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database (MIT-ArrhyDB), classifying five distinct classes of arrhythmias based on their morphological features. Result: The proposed model exhibits an impressive F1 Score of 98.52% and classification accuracy of 98.95%. Conclusion: Comparative analysis with standard CNN exposes the superior performance of our proposed model. This highlights its outstanding overall performance and potential utility in clinical applications.
Keywords: Electrocardiogram (ECG), Arrhythmia, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Transformer
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education, Kolar, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.